In 1990 I returned to this problem again by calculating the strange quark production rate in a plasma of massive gluons with Drs P.Lévai and B.Müller . If gluons were more massive then two strange quarks also the g -> ss one gluon decay would contribute [32] . According to recent perturbative estimates, however, this is not the case, so in general the in-medium production rates are somewhat reduced.
Furthermore, in the framework of variational approach to the QCD at low and high temperatures the gluon mass can be used as an order parameter signalling a first order phase transition of the pure glue. In the years 1987 - 1989 I worked out such a variational model of QCD which describes the most important phenomenological aspects from the gluon condensate to heavy quark confinement using a single scale parameter, the gluon mass, only [5, 25, 27, 29, 31, 35].
These investigations are also reviewed in my habilitation thesis. Further work related to the confinement phenomenology can be found in [23, 28].
With Drs B. Müller and X. N. Wang we estimated the Debye mass in an anisotrop parton medium; the polarisation tensor looses its sphericity in this case. A slight difference between longitudinal (paralell moving test charge) and transverse (orthogonally moving test charge) Debye masses has been found [36] .
A review of the role of chaos in gauge theory can be found in our recently published book [7] (co-authors S. Matinyan and B. Müller ). Further developments are published in [43, 44, 45] .
Investigations of the effect of static charges [46] and Higgs fields [47] followed. Recently we study the Lyapunov exponent for lattice configurations generated by quantum Monte Carlo simulations (collaborator H. Markum ).
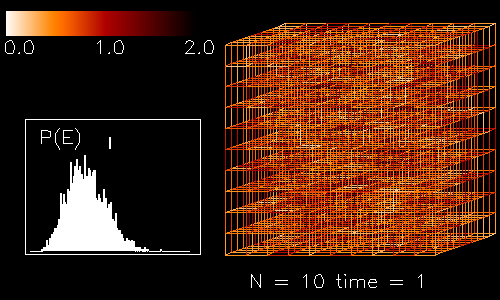
This figure shows a sample configuration on a 10 x 10 x 10 lattice. The 1-Tr(Up) values are averaged for all four plaquettes attached on a given link. These are color coded in the interval (0,2).
The diagram shows the distribution of the plaquette energies at a finite temperature.