Model-based source localization of extracellular action potentials
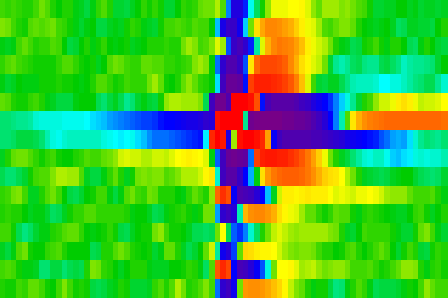 Traditional current source density calculation method (CSD) method allows calculation of neural current source distribution from the extracellular potential patterns, thus provides important information for neurophysiology. The traditional CSD method is based on strong physical foundations, but uses some assumptions, which can not hold for single cell activ- ity. By this reason, traditional CSD method gives false results for single cell activity. A new, spike CSD (sCSD) method have been developed, directly designed for revealing cur- rent source density distribution of a single cell, during firing. This new method is based on the inverse solution of the Poisson-equation and were applied on extracellular spatial potential patterns of spikes.
Traditional current source density calculation method (CSD) method allows calculation of neural current source distribution from the extracellular potential patterns, thus provides important information for neurophysiology. The traditional CSD method is based on strong physical foundations, but uses some assumptions, which can not hold for single cell activ- ity. By this reason, traditional CSD method gives false results for single cell activity. A new, spike CSD (sCSD) method have been developed, directly designed for revealing cur- rent source density distribution of a single cell, during firing. This new method is based on the inverse solution of the Poisson-equation and were applied on extracellular spatial potential patterns of spikes.
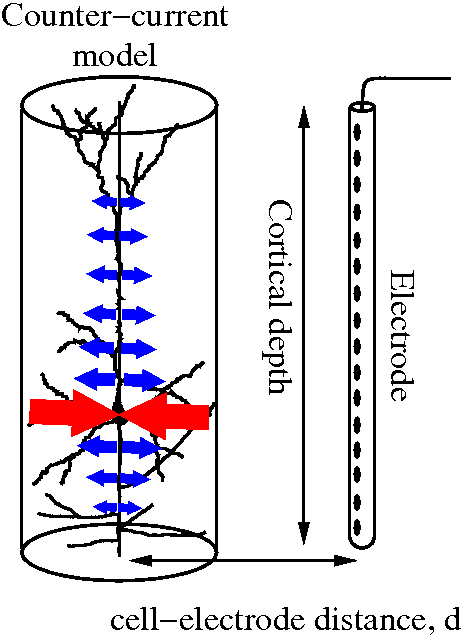
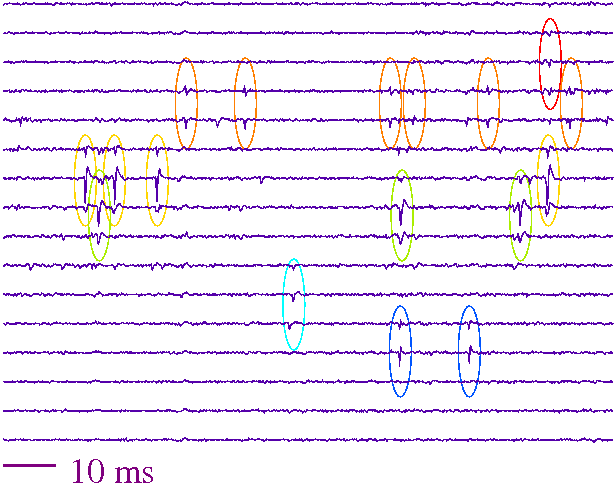
The spikes were measured in cat primary auditory cortex with a 16 channel chronically implanted linear probe in vivo. Using our new method, many fine details of the spatio-temporal dynamics of spikes were uncovered. Dendritic back propa- gation was proven to be much more frequent than it was known before, it was observable in every cell. The speed of back propagation was typically different in the apical and basal directions. In contrast to the literature, forward propagation preceding the spikes was also observable. In perspective, this new method raises the possibility of identifying synaptic inputs, which causes a cell fire.
- A hozzászóláshoz belépés szükséges
